how to find the p value given z
A p-value is a probability associated with your critical value. The critical value depends on the probability you are allowing for a Blazon I error. It measures the chance of getting results at least as potent as yours if the claim (H0) were truthful.
The following figure shows the locations of a exam statistic and their respective conclusions.
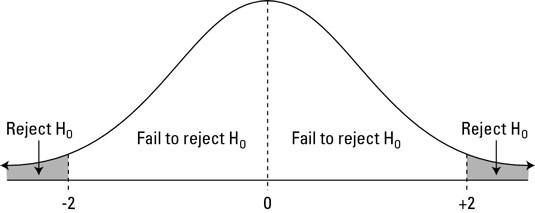
Decisions for Ha: non-equal-to.
To find the p-value for your test statistic:
-
Look up your test statistic on the appropriate distribution — in this case, on the standard normal (Z-) distribution (run into the following Z-tables).
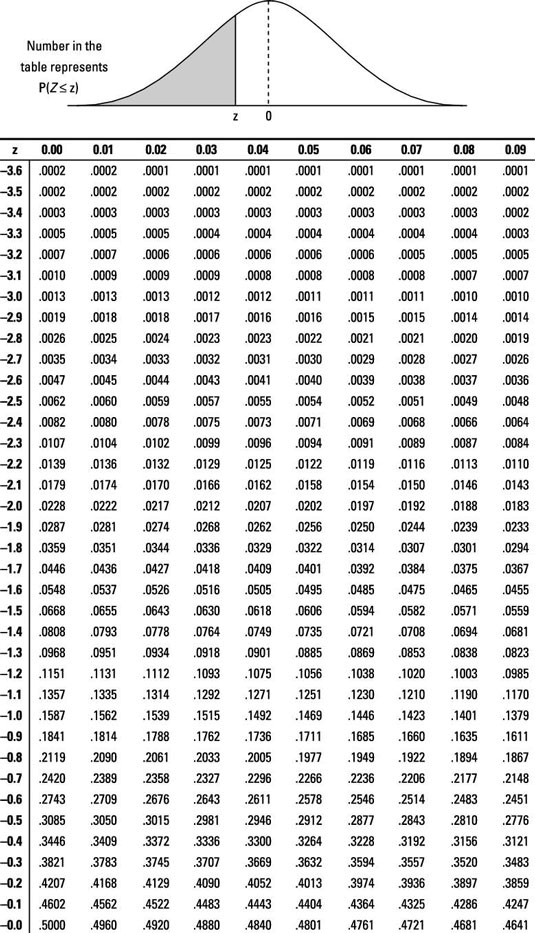
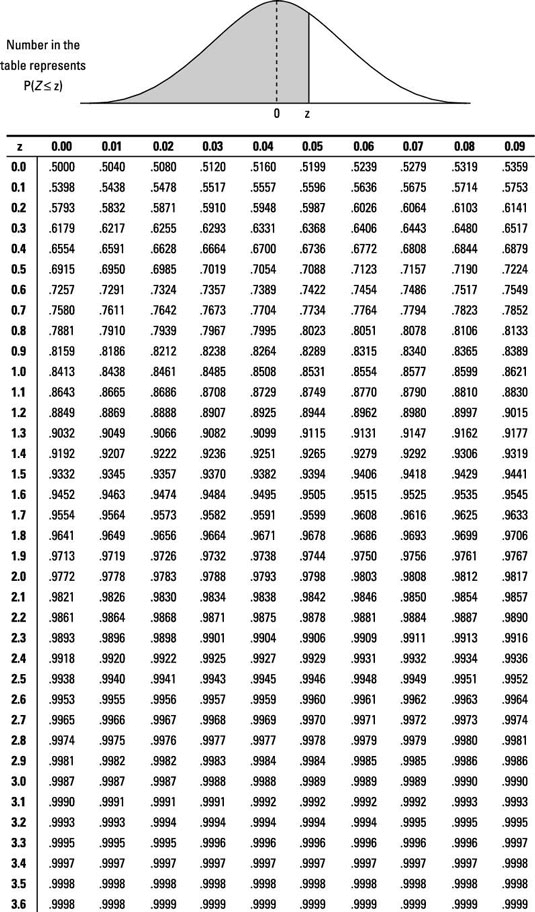
-
Discover the probability that Z is beyond (more than extreme than) your test statistic:
-
If Ha contains a less-than alternative, find the probability that Z is less than your test statistic (that is, look upward your test statistic on the Z-tabular array and find its respective probability). This is the p-value. (Note: In this case, your exam statistic is commonly negative.)
-
If Ha contains a greater-than alternative, find the probability that Z is greater than your test statistic (await up your test statistic on the Z-table, find its respective probability, and subtract it from one). The upshot is your p-value. (Notation: In this instance, your test statistic is commonly positive.)
-
If Ha contains a non-equal-to alternative, detect the probability that Z is across your test statistic and double it. There are two cases:
If your test statistic is negative, beginning find the probability that Z is less than your test statistic (look up your examination statistic on the Z-table and notice its corresponding probability). Then double this probability to get the p-value.
If your exam statistic is positive, start find the probability that Z is greater than your test statistic (await up your test statistic on the Z-table, find its corresponding probability, and subtract it from one). Then double this result to get the p-value.
-
When testing H0: p = 0.25 versus Ha: p < 0.25, you find that the p-value of -1.25 by finding the probability that Z is less than -1.25. When you look this number up on the above Z-table, you lot find a probability of 0.1056 of Z being less than this value.
Note: If you had been testing the two-sided culling,
![]()
the p-value would be two ∗ 0.1056, or 0.2112.
If the results are likely to have occurred under the claim, then you fail to reject H0 (like a jury decides not guilty). If the results are unlikely to have occurred under the claim, and then you decline H0 (similar a jury decides guilty).
Well-nigh This Article
This article tin exist found in the category:
- Statistics ,
Source: https://www.dummies.com/article/academics-the-arts/math/statistics/how-to-determine-a-p-value-when-testing-a-null-hypothesis-169062/
Posted by: orozcowarts1946.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find the p value given z"
Post a Comment